Types of Planes in Drawing
Reckoner Graphics
From the early days of aviation, development of aircraft, aircraft engines, and other components relied heavily on shipping drawings. For about of the 20th century, drawings were created on a drawing "board" with pen or pencil and paper. With the introduction and advancement of computers in the later decades of the 20th century, the way drawings are created changed dramatically. Computers were used non but to create drawings, but they were being used to show items in "virtual reality," from any possible viewing angle. Further development of computer software programs immune for assembling of separately created parts to check for proper fit and possible interferences. Additionally, with nearly instantaneous information sharing capability through estimator networking and the Net, it became much easier for designers to share their piece of work with other designers and manufacturers virtually anytime, anywhere in the world. Using new computer-controlled manufacturing techniques, information technology became possible to design a part and take it precisely manufactured without ever having shown it on paper. New terms and acronyms became commonplace. The more common of these terms are:
- Computer Graphics—drawing with the use of a computer
- Computer Aided Design (CAD)—where a estimator is used in the design of a part or product
- Computer Aided Design Drafting (CADD)—where a estimator is used in the blueprint and drafting procedure
- Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM)—where a computer is used in the manufacturing of a part or product
- Estimator Aided Applied science (CAE)—where a computer is used in the engineering of a function or production
As computer hardware and software continue to evolve, a greater amount of CAE is completed in less time, at lower cost. In addition to product design, some of the other uses of CAE are production analysis, assembly, simulations, and maintenance information. [Effigy ane]
 |
| Figure 1. Calculator graphics piece of work station |
CATIA, ProEngineer, Solid Works, and Unigraphics are some of the more pop CAD software packages used for aircraft design and manufacturing. Nigh airframe manufacturers utilize CATIA software to pattern their aircraft. The complete aircraft is designed and assembled in the software bundle before it is manufactured. Drawings of all parts of the aircraft are available and tin can exist accessed using the computer software. Drawings are no longer limited to one, two, or three views. Drawings from every angle can easily be accessed by using the calculator model of the part or production. Technicians tin can access drawings and aircraft manuals on laptops or fifty-fifty mobile devices when performing maintenance on the shop floor.
Purpose and Part of Aircraft Drawings
Drawings and prints are the link betwixt the engineers who design an aircraft and the workers who build, maintain, and repair it. A impress may exist a copy of a working cartoon for an aircraft part or group of parts, or for a blueprint of a system or grouping of systems. They are made by placing a tracing of the drawing over a sheet of chemically-treated paper and exposing it to a strong light for a short period of time. When the exposed paper is developed, it turns blueish where the light has penetrated the transparent tracing. The inked lines of the tracing, having blocked out the low-cal, testify as white lines on a blue groundwork. With other types of sensitized paper, prints may have a white background with colored lines or a colored groundwork with white lines.
Drawings created using computers may exist viewed on the calculator monitor or printed out in "hard copy" by use of an ink jet or light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation printer. Larger drawings may exist printed past use of a plotter or large format printer. Big printers tin print drawings up to 42 inches loftier with widths upwardly to 600 inches by utilise of continuous roll paper. [Figure 2]
 |
| Figure 2. Big format printer |
Care and Use of Drawings
Drawings should be handled advisedly every bit they are both expensive and valuable. Open drawings slowly and carefully to foreclose tearing of the paper. When the drawing is open, smooth out the fold lines instead of angle them backward.
To protect drawings from damage, never spread them on the floor or lay them on a surface covered with tools or other objects that may make holes in the newspaper. Easily should be free of oil, grease, or other unclean matter that can soil or smudge the print.
Never brand notes or marks on a print, as they may confuse others and lead to incorrect piece of work. Just authorized individuals are permitted to make notes or changes on prints, and they must sign and date any changes they make.
When finished with a drawing, fold and render it to its proper place. Prints are folded originally in an advisable size for filing. Care should be taken so that the original folds are always used.
Types of Drawings
Drawings must give information such as size and shape of the object and all its parts, specifications for material to be used, how the material is to be finished, how the parts are to be assembled, and any other information essential to making and assembling the object. Drawings may be divided into three classes: particular, assembly, and installation.
Detail Drawing
A item drawing is a clarification of a single part, describing past lines, notes, and symbols the specifications for size, shape, material, and methods of industry to be used in making the part. Detail drawings are usually rather simple. When single parts are small, several detail drawings may be shown on the same sheet or print. [Figure 3]
 |
| Figure 3. Detail drawing |
Associates Cartoon
An assembly cartoon is a description of an object made up of two or more parts. [Figure four] It describes the object's size and shape. Its chief purpose is to bear witness the relationship of the various parts. An assembly drawing is usually more than complex than a item drawing and is often accompanied by detail drawings of diverse parts.
 |
| Effigy 4. Assembly drawing |
Installation Drawing
An installation cartoon is one that includes all necessary information for a function or an associates in the terminal installed position in the aircraft. It shows the dimensions necessary for the location of specific parts with relation to the other parts and reference dimensions that are helpful in later on work in the store. [Figure v]
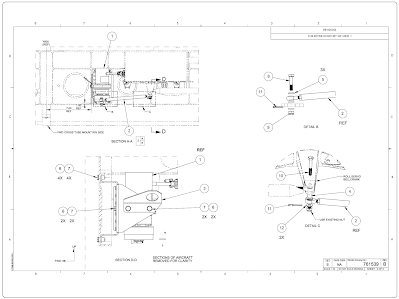 |
| Figure 5. Installation drawing |
Sectional View Drawings
A section or sectional view is obtained by cutting abroad office of an object to show the shape and construction at the cutting airplane. The part or parts cut abroad are shown past using department (crosshatching) lines. Types of sections are described in the following paragraphs.
Total Section
A full section view is used when the interior structure or subconscious features of an object cannot be shown clearly by exterior views. For case, Figure 6 is a sectional view of a cable connector and shows the internal construction of the connector.
 |
| Figure half dozen. Sectional view of a cable connector |
One-half Department
In a half section, the cutting aeroplane extends only halfway across the object, leaving the other half of the object as an exterior view. Half sections are used with symmetrical objects to bear witness both the interior and outside. Figure seven is a half sectional view of a Capstan servo.
 |
| Figure vii. Half section of a Capstan servo |
Revolved Section
A revolved department drawn straight on the exterior view shows the shape of the cross section of a part, such as the spoke of a wheel. An instance of a revolved section is shown in Effigy 8.
 |
| Figure viii. Revolved sections |
Removed Section
A removed department illustrates parts of an object. It is drawn similar revolved sections, except it is placed at ane side and often drawn to a larger scale than the view indicated to bring out pertinent details.
Figure 9 is an analogy of removed sections. Section A-A shows the cross-exclusive shape of the object at cut aeroplane line A-A. Section B-B shows the cantankerous-sectional shape at cutting plane line B-B. These sectional views are drawn to the same scale every bit the principal view.
 |
| Figure 9. Removed sections |
RELATED POSTS
- Aircraft Drawings
- Championship Blocks, Universal Numbering Arrangement, Cartoon Standards and Neb of Material
- Other Aircraft Drawing Data
- Methods of Illustration
- Cartoon Sketches
- Charts and Graphs
porterfeenday1989.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.aircraftsystemstech.com/2019/10/aircraft-drawings-computer-graphics.html
0 Response to "Types of Planes in Drawing"
Post a Comment